OP14 Risk of colorectal cancer diagnosis and colorectal cancer mortality in Crohn’s disease: A Scandinavian population-based cohort study
O. Olen1, R. Erichsen2, M.C. Sachs1, L. Pedersen2, J. Halfvarson3, J. Askling1, A. Ekbom1, H.T. Sørensen2, J.F. Ludvigsson4
1Department of Medicine Solna, Clinical Epidemiology Division, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, 2Department of Clinical Epidemiology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark, 3Department of Gastroenterology, Faculty of Medicine and Health, Örebro University, Örebro, Sweden, 4Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden
Background
Crohn’s disease (CD) is a risk factor for colorectal cancer (CRC). Earlier studies reflect older treatment and surveillance strategies, and most have studied incident CRC without addressing potential lead-time and surveillance biases. Such bias can be reduced by examining tumour stage-adjusted CRC incidence and CRC mortality. We aimed to assess risks of CRC mortality and incident CRC among patients with CD compared with the general population.
Methods
Nationwide register-based cohort study during 1969–2017 of 47,035 patients with CD in Denmark (
Results
During 1969–2017, 499 patients with CD developed CRC, corresponding to an adjusted HR of 1.40 [95% confidence interval (CI) 1.27–1.53]. We observed 296 (0.47/1000 person-years) deaths from CRC in patients with CD compared with 1968 (0.31/1000) in reference individuals [HR 1.74 (95% CI 1.54–1.96)]. CD patients diagnosed with CRC were at increased risk of CRC mortality compared with reference individuals also diagnosed with CRC [HR = 1.30 (95% CI 1.06–1.59)] and tumour stage at CRC diagnosis did not differ between groups (
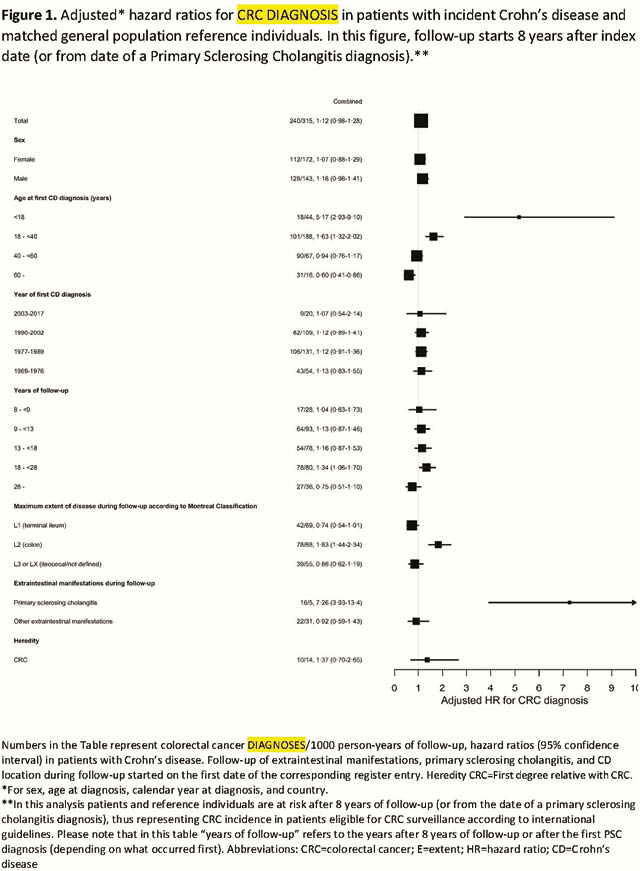
Conclusion
CD patients are at increased risk of a CRC diagnosis and CRC death. Despite repeated colonoscopies during follow-up, CD patients are not diagnosed earlier (less severe tumour stage) with CRC than reference individuals. Nevertheless, CD patients with CRC have higher mortality than non-CD patients also diagnosed with CRC. CRC surveillance could likely be improved and should be focussed on CD patients <40 years at CD onset, patients with colon inflammation, and patients who have PSC.


