P216 Anti-drug antibodies to infliximab: A comparison of free anti-drug antibody measurement
R. Hamilton1, S. Shields2, J. MacDonald2, A. Dunlop1, M. Perry3, A. McGucken3, E. Gribben4, P. Galloway1
1Department of Biochemistry, NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde, Glasgow, UK, 2Department of Gastroenterology, NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde, Glasgow, UK, 3Department of Rheumatology, NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde, Paisley, UK, 4Department of Biological and Biomedical Sciences, Glasgow Caledonian University, Glasgow, UK
Background
Infliximab (IFX) is a biologic drug that inhibits the action of TNFα, a pro-inflammatory cytokine implicated in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). IFX has greatly improved the outcomes for patients with IBD, but response to the drug is not universal. Primary non-response to IFX treatment occurs in up to 30% of IBD patients while up to 46% of patients develop secondary loss of response.1,2 Anti-drug antibodies (ADAs) to IFX are considered a significant risk factor for the loss of response to treatment, hence the measurement of ADAs as part of therapeutic drug monitoring is an increasingly utilised tool. The detection of ADAs varies widely depending on the type of assays used. The aim of this study was to determine the qualitative concordance of three commercially available ELISA kits for measurement of free ADAs to IFX on the Grifols Triturus analyser.
Methods
150 patient samples with low IFX drug levels (≤0.6 µg/ml) were analysed for free ADAs using Promonitor, Lisa Tracker and IDKmonitor kits on the Grifols Triturus automated ELISA analyser.
Results
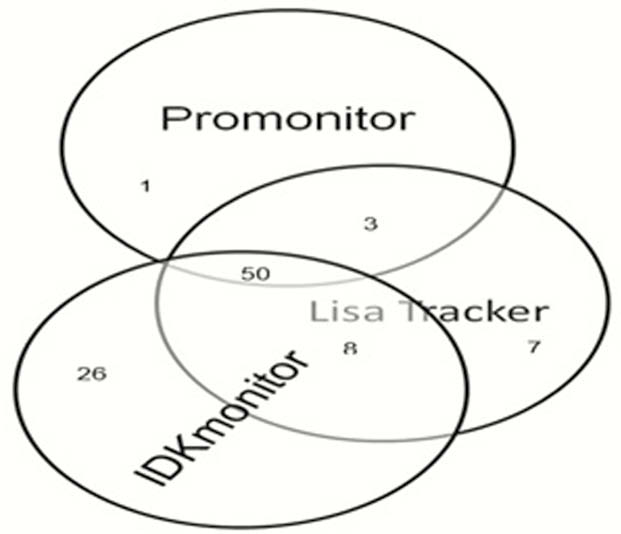
Kappa coefficient (κ) analysis indicated a moderate agreement between the Promonitor and IDKmonitor assays (κ = 0.484 (95% CI, 0.357 to 0.611)) and the IDKmonitor and Lisa Tracker assays (κ = 0.485 (95% CI, 0.348–0.621)) as well as substantial agreement between the Promonitor and Lisa Tracker assays (κ = 0.768 (95% CI, 0.667–0.870)). Figure 1 shows the distribution of samples identified as free ADA positive by each kit.
Conclusion
Although a broad qualitative agreement was found between the three kits, they should not be used interchangeably for patient management. All kits appear amenable for utilisation in a high-throughput laboratory though a true quantitative comparison between these kits was precluded by the absence of any certified reference material for free ADAs to IFX. Further research is required to estimate the impact of free ADAs on efficiency of IFX treatment and patient management.
Ben-Horin S and Chowers.
Osterman MT, Haynes K, Delzell E,


