P266 The impact of vedolizumab and ustekinumab on arthropathy and arthralgia in IBD patients: a real-life multicentric cohort study
Truyens, M.(1,2,3,4);De Galan, C.(1,3,4);Peeters, H.(5);Mesonero Gismero, F.(6);Elorza, A.(7);Torres, P.(8);Vandermeulen, L.(9);Jauregui Amezaga, A.(10);Ferreiro-Iglesias, R.(11);Holvoet, T.(12);Zabana, Y.(13,14);Peries Reverter, L.(15);Geldof, J.(1,2);Varkas, G.(4,16);De Vos, M.(1,2,3);Lobaton, T.(1,2);
(1)Ghent University, Department of Internal Medicine and Pediatrics, Ghent, Belgium;(2)University Hospital Ghent, Department of Gastroenterology, Ghent, Belgium;(3)Ghent University, Ghent Gut Inflammation Group GGIG, Ghent, Belgium;(4)Ghent University, VIB center for Inflammation Research IRC, Ghent, Belgium;(5)AZ Sint Lucas, Department of Gastroenterology, Ghent, Belgium;(6)Hospital Ramon y Cajal, Department of Gastroenterology, Madrid, Spain;(7)Hospital de Galdakao, Department of Gastroenterology, Bilbao, Spain;(8)Hospital Universitari Germans Trias i Pujol, Department of Gastroenterology, Barcelona, Spain;(9)Vrije Universiteit Brussel VUB - Universitair Ziekenhuis Brussel, Department of Gastroenterology, Brussels, Belgium;(10)University Hospital Antwerp, Department of Gastroenterology, Antwerp, Belgium;(11)Hospital Clínico Universitario de Santiago, Department of Gastroenterology, Santiago de Compostela, Spain;(12)AZ Nikolaas, Department of Gastroenterology, Sint-Niklaas, Belgium;(13)Hospital Universitari Mútua de Terrassa, Department of Gastroenterology, Barcelona, Spain;(14)Hospital Universitari Mútua de Terrassa, Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Hepáticas y Digestivas CIBERehd, Barcelona, Spain;(15)Hospital Universitari de Girona, Department of Gastroenterology, Girona, Spain;(16)University Hospital Ghent, Department of Rheumatology, Ghent, Belgium
Background
Extra-intestinal manifestations (EIM) are frequently reported in inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). Although the efficacy of TNF inhibitors is well documented, data regarding the effect of vedolizumab (VDZ) and ustekinumab (UST) are limited. Theoretically, the advantage of VDZ, i.e. gut-selectivity, may reduce the efficacy on EIM while the systemic effect of UST may be of benefit. Therefore, we evaluated the differences in new onset and evolution of EIM during both treatments.
Methods
An international multicentric retrospective study was performed on IBD patients who started VDZ or UST between May 2010 and December 2020. EIM were assessed at baseline and during follow-up. Arthropathy was defined as joint inflammation (arthritis/sacroiliitis) and arthralgia as articular pain without confirmed inflammation. Skin EIM included erythema nodosum (EN), pyoderma gangrenosum (PG) and Sweet syndrome. Ocular EIM included (epi)scleritis and uveitis. Uni- and multivariate analyses were performed.
Results
In total 856 patients were included: 528 treated with VDZ and 328 with UST. At baseline, arthropathy was more prevalent in UST treated patients (12.2% vs 7.2%; p=0.037; Table 1). No differences in rates of new onset (Fig 1) or evolution of pre-existing arthropathies could be identified between VDZ and UST. In multivariate analyses new onset arthropathy was not associated with smoking, IBD type, sex nor studied biological. In 5 out of 48 (10.4%) VDZ patients and 2 of 46 (4.3%) UST patients with either pre-existing or new arthropathy, treatment was stopped due to articular disease (difference not significant).
In contrast, new arthralgia onset within 1 year of follow-up was significantly associated with VDZ treatment (OR 2.1 (1.1-4.0); p=0.022; Fig 1). Arthralgia was the reason to stop treatment in 2 of 87 (2.3%) VDZ patients and never in UST patients.
Beside joint EIM, 2 patients developed EN, 1 PG and 1 episcleritis during VDZ treatment. Under UST treatment 1 patient developed EN. No patients developed new Sweet syndrome, scleritis nor uveitis.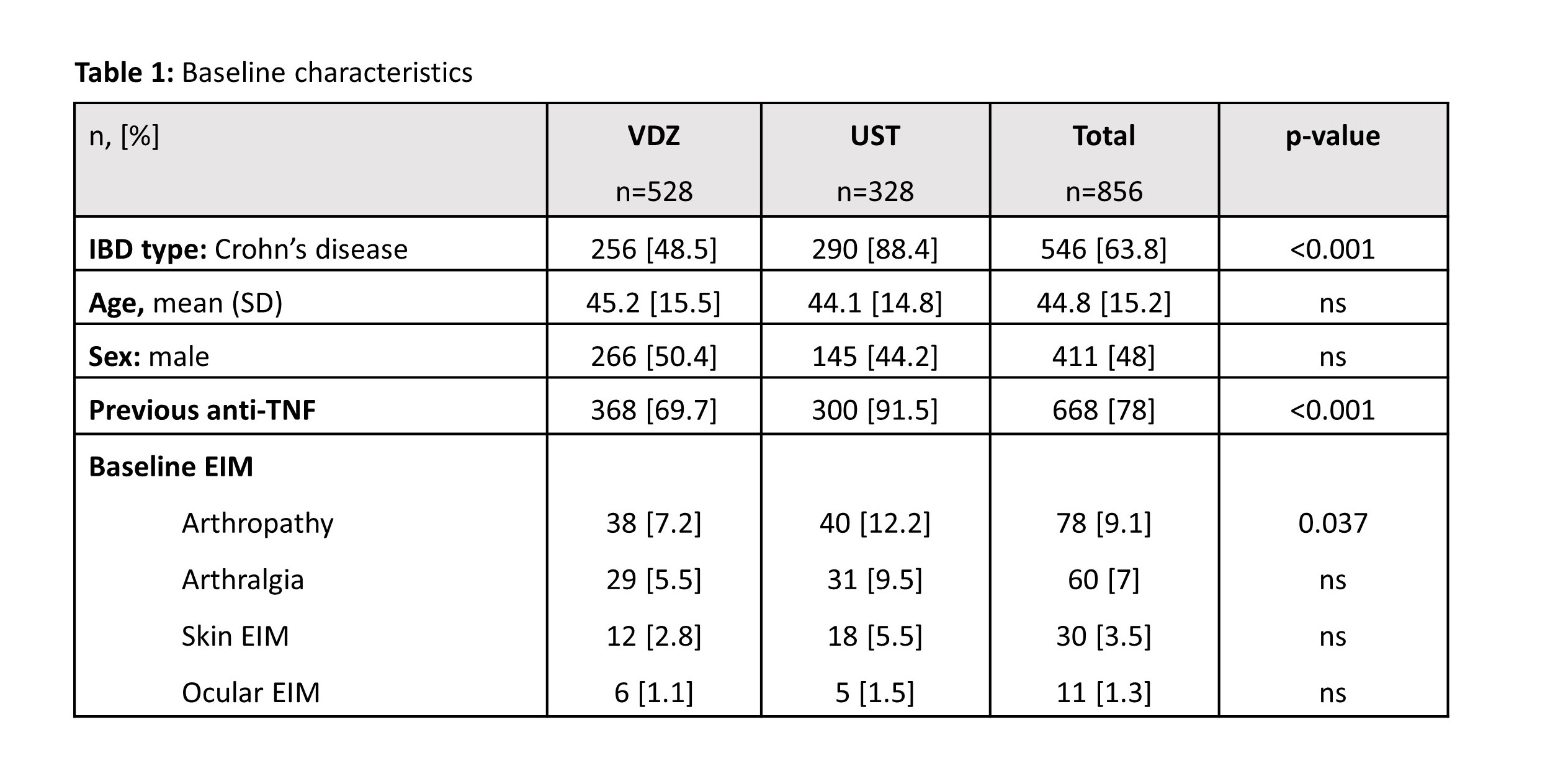

Conclusion
No differences in the rate of new arthropathy onset were observed between VDZ and UST. In contrast, VDZ treatment did increase the risk of new onset arthralgia.


