P291 Diagnostic utility of the neutrophil-platelet rate (NeuPla) as a marker of activity in patients with ulcerative colitis
J.K. Yamamoto-Furusho MD- PhD1, E.A. Mendieta-Escalante2
1National Institute of Medical Science and Nutrition Salvador Zubiran, Department of Gastroenterology, Mexico City, Mexico, 2IBD Clinic- Department of Gastroenterology, Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Medicas y Nutrition, Gastroenterology, Mexico, Mexico
Background
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic disease characterised by periods of activity and remission. There are biomarkers such as C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and faecal calprotectin that are elevated in patients with active UC. The platelet, one of the main activators of neutrophils, contains IL-8, a potent neutrophil chemo-attractant and P-selectin that induces excretion of superoxide in the neutrophils, forming platelet-neutrophil aggregates that are increased in individuals with UC activity. No previous studies have evaluated the neutrophil-platelet (NeuPla) rate as a tool for evaluating disease activity. The aim of this study was to evaluate the clinical utility of NeuPla rate in patients with UC.
Methods
A total of 158 patients with a definitive diagnosis of UC were included and NeuPla index was calculated on the ratio between neutrophil differential count and platelets from complete blood count (CBC) at least 1 day after the colonoscopy and colon biopsies. The activity was classified according to Mayo endoscopic sub-score, Riley score, Truelove-Witts, Montreal, full Mayo, and Yamamoto-Furusho indexes.
Results
The correlation of the NeuPla index with all activity indexes was statistical significant (p <0.001) as well as faecal calprotectin (rho: 0.532,
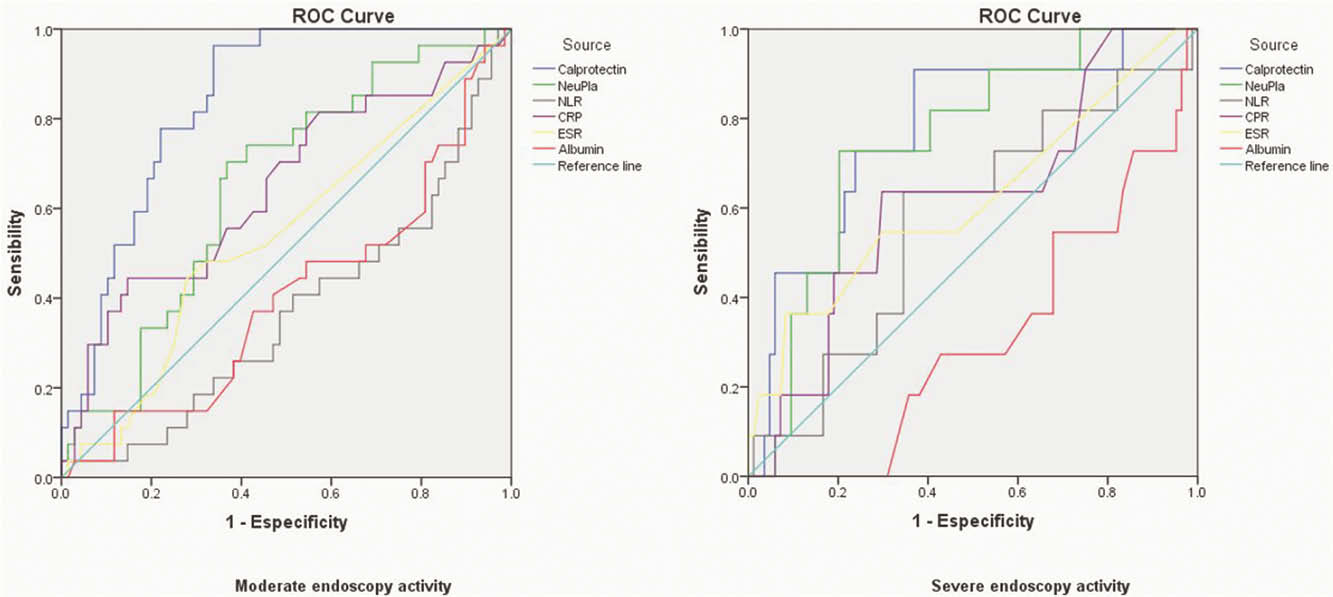
Conclusion
The NeuPla index has a good diagnostic utility in order to distinguish patients with clinical and endoscopic activity without the need to perform invasive studies such as colonoscopy. This index is a cheap and easy access monitoring tool and a better diagnostic performance in comparison with other serum biomarkers CPR, ESR and serum albumin.


