P292 Effect of drug therapy on the lipid profiles of patient with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Sleutjes, J.A.M.(1);Roeters van Lennep , J.E.(2);Boersma , E.(3);de Vries , A.C.(1);van der Woude , C.J.(1);
(1)Erasmus Medical Center, Gastroenterology & Hepatology, Rotterdam, The Netherlands;(2)Erasmus Medical Center, Internal Medicine, Rotterdam, The Netherlands;(3)Erasmus Medical Center, Clinical Epidemiology of Cardiovascular Diseases, Rotterdam, The Netherlands
Background
Increases of lipid levels associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) medication have been previously reported. However, it is unknown whether this effect is similar for all IBD drug classes.
Methods
We performed a systematic literature search of randomized controlled trials and observational cohort studies of IBD treatment with corticosteroids, anti TNFα agents and tofacitinib that assessed total cholesterol (TC) before and after short-term (≤8 week) and long-term (≥12 week) treatment. Data of 11 studies (1,663 IBD patients) were pooled using a random effect model with as primary outcome TC levels. Lipid changes were reported as mean difference on the log2-scale (MDlog2) with 95% CI. The effect of patient and disease characteristics on TC changes were analyzed in 6 studies with individual patient data of 1,211 patients.
Results
A significant increase in TC was observed after treatment with corticosteroids, anti TNFα agents and tofacitinib (short-term +0.370, +0.197 and +0.190; long-term: +0.452, +0.068 and +0.162, respectively). (Figure 1) After correcting for age, sex, BMI and CRP, increases of TC levels after start of corticosteroids and tofacitinib treatment were higher (short-term: +0.293 and +0.161; long-term: +0.090 and +0.127, respectively) as compared to anti TNFα agents (short-term: -0.059, long-term: +0.041). (Figure 2)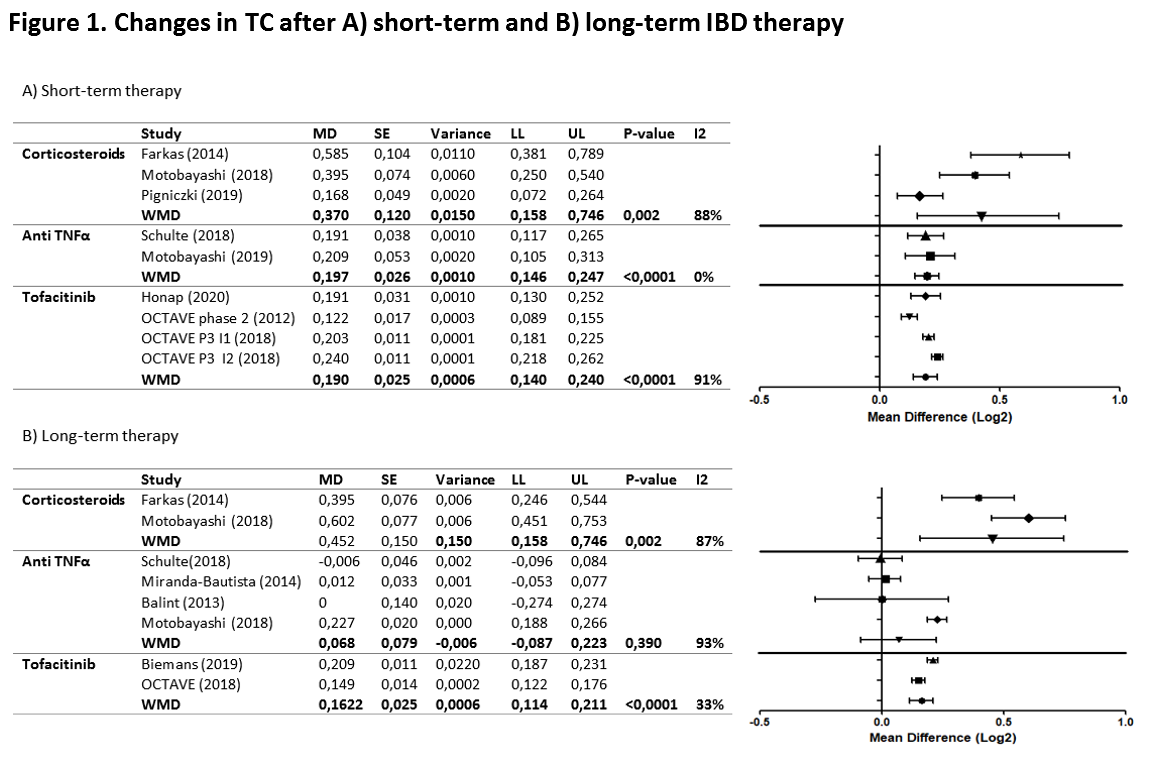

Conclusion
Changes in lipid levels differ between IBD drug classes. TC levels increase was strongest for corticosteroids followed by tofacitinib but not observed for anti TNFα agents. Whether TC change associated with IBD treatment has effect on CVD risk requires further study.


