P342 Diagnostic accuracy of rectal bleeding and stool frequency in predicting mucosal healing in patients with ulcerative colitis in the tofacitinib OCTAVE Phase 3 induction studies
J.F. Colombel1, A.G. Bushmakin2, J.C. Cappelleri2, N. Kulisek3, G.O. Santana4, N. Lawendy3, D. Ponce de Leon5, P.L. Lakatos6
1Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, NY, USA, 2Pfizer Inc., Groton, CT, USA, 3Pfizer Inc., Collegeville, PA, USA, 4University of the State of Bahia, Salvador, Bahia, Brazil, 5Pfizer Inc., Lima, Peru, Peru, 6McGill University Health Center, Montreal, Québec, Canada
Background
Tofacitinib is an oral, small-molecule JAK inhibitor for the treatment of ulcerative colitis (UC). In patients with UC, associations between endoscopic findings and patient-reported outcomes, such as stool frequency (SF) and rectal bleeding (RB), are not well described. Here, we evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of Mayo SF and RB subscores to predict mucosal healing (MH) in OCTAVE Induction 1 and 2 (NCT01465763; NCT01458951).
Methods
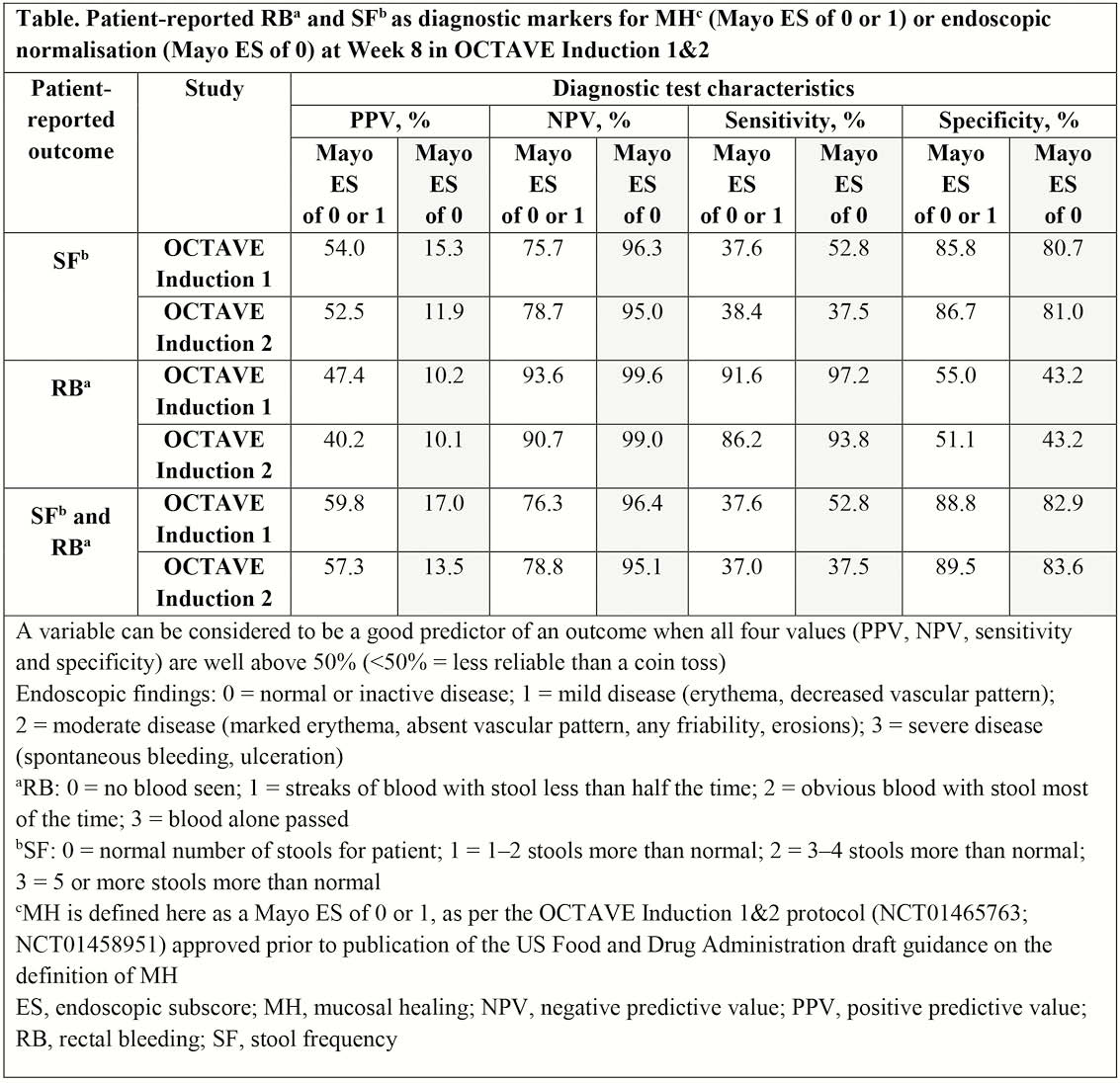
This post hoc analysis used data from OCTAVE Induction 1 and 2, two identical, randomised, placebo-controlled, 8-week, Phase 3 studies of tofacitinib for the treatment of patients with moderately to severely active UC.1 SF (Mayo subscore 0–3), RB (Mayo subscore 0–3) and endoscopic findings (Mayo endoscopic subscore [ES] 0–3) were assessed at baseline and at Week 8. MH and endoscopic normalisation were defined as an ES of 0 or 1, or an ES of 0, respectively. Based on two-by-two contingency tables, diagnostic test characteristics for SF and RB were evaluated: positive and negative predictive values, sensitivity and specificity. Kappa statistics (chance-corrected measure of agreement) and Pearson correlations (a measure of association) were also calculated. All available data at Week 8 were used.
Results
A total of 614 and 547 patients received treatment (tofacitinib 15 or 10 mg BID, or placebo) in OCTAVE Induction 1 and 2, respectively. Two-by-two contingency table analyses showed that dichotomised SF (0 vs. ≥1) and RB (0 vs. ≥1) were each or both not good predictors of MH (ES of 0 or 1 vs. ≥2) or endoscopic normalisation (ES 0 vs. ≥1), as ≥1 of the four diagnostic test characteristics was <50% (Table). In OCTAVE Induction 1 and 2, weighted kappa statistics for SF (original metric 0–3) and RB (0–3) vs. ES (0–3) indicated moderate agreement for SF (0.46 and 0.42, respectively), slight agreement for RB (0.19 and 0.15, respectively) and fair agreement for SF and RB (0.40 and 0.34, respectively). Correlations were 0.54 and 0.49 for SF, 0.46 and 0.37 for RB and 0.57 and 0.51 for SF and RB (OCTAVE Induction 1 and 2, respectively), suggesting a modest-to-moderate association.
Conclusion
In patients with UC treated with tofacitinib or placebo in OCTAVE Induction 1 and 2, SF and RB subscores had slight-to-moderate agreement with ES, but were not predictive of MH or endoscopic normalisation. The presence of blood at Week 8 strongly indicated that patients had endoscopic activity, but the absence of blood was associated with MH in <50% of patients. Further analysis is needed to fully understand the relationship between SF, RB and MH.
Sandborn WJ


