P445 Efficacy and safety of induction therapy with calcineurin inhibitors followed by maintenance therapy with vedolizumab in severe ulcerative colitis: a large patient cohort with long-term follow-up
J. OLLECH1, S. Dwadasi1, I. Normatov1, A. Israel1, V. Rai1, P. Sossenheimer1, B. Christensen2, S. Dalal1, J. Pekow1, A. Sakuraba1, R. Cohen1, D. Rubin1
1Gastroenterology, University of Chicago Medicine, Chicago, USA, 2Gastroenterology, The Royal Melbourne Hospital, Melbourne, Australia
Background
The options for the medical management of patients with severe ulcerative colitis failing IV steroids are limited and include the calcineurin inhibitors cyclosporin or tacrolimus, especially in patients who had previously failed anti-TNF agents. Following induction therapy with a calcineurin inhibitor, transitioning to vedolizumab as maintenance therapy could be an option. We report on the largest cohort of patients successfully induced with calcineurin inhibitors who were then transitioned to vedolizumab maintenance therapy.
Methods
We performed a retrospective observational study of adult ulcerative colitis patients followed at the University of Chicago Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center. Patients with severe steroid-refractory ulcerative colitis were included if they received a calcineurin inhibitor (ciclosporin or tacrolimus) as induction therapy followed by maintenance therapy with vedolizumab between January 2014 and December 2018. Patients who had a follow-up of fewer than three months were excluded. The primary endpoint was colectomy-free survival. Secondary endpoints included survival without vedolizumab discontinuation as well as clinical, steroid-free and biochemical remission at week 14.
Results
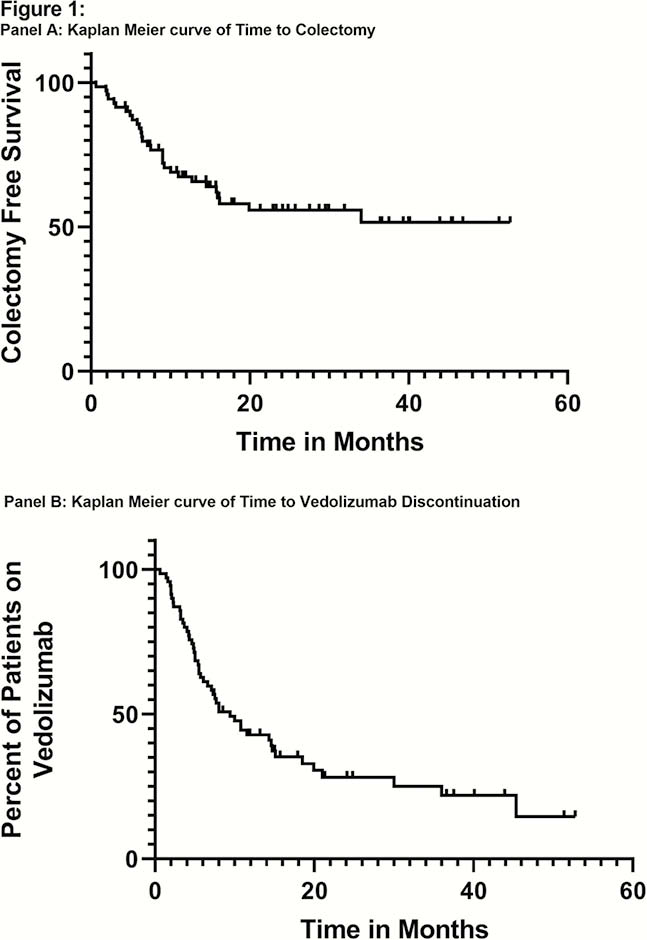
A total of 71 patients (59% male) were treated with vedolizumab after induction therapy with calcineurin inhibitors for severe steroid-refractory colitis. Truelove and Witts criteria for Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis were fulfilled in 77% of patients, and 97% of patients had moderate to severe endoscopic disease. Patients were followed for a median time of 25 months (IQR 16–36). Colectomy free survival rates from vedolizumab initiation were 67% at one year and 55% at two years (Figure 1, Panel A). At the end of induction with vedolizumab at week 14, 50% of patients were in clinical remission, and 62% of patients had a normal CRP. At one and two years following vedolizumab initiation, 43% and 28% of patients were still on vedolizumab, respectively (Figure 1, Panel B). Vedolizumab was dose escalated to infusions every four weeks in 44% of patients. The median time to dose escalation was 5.6 months (IQR 4.1–8.2). No serious adverse events were recorded in our patient cohort.
Conclusion
Transitioning to vedolizumab following induction of remission with calcineurin inhibitors is effective and safe. Such a treatment strategy should be considered in patients with severe steroid-refractory ulcerative colitis, especially in cases of previous anti-TNF failure.


