P584 Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Evaluating the Real-World Effectiveness and Safety of Ustekinumab in Crohn’s Disease
Hosack, T.(1);Gadhok, R.(2);Lindsay, J.O.(2);
(1)Buckinghamshire Health NHS Trust, Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Aylesbury, United Kingdom;(2)Barts Health NHS Trust, Gastroenterology and Hepatology, London, United Kingdom;
Background
The landmark UNITI trials 1 of Ustekinumab (UST, an anti-p40IL12/23 mAb) in treating Crohn's disease (CD) demonstrated 6-week clinical response and 44-week clinical remission rates of 38% and 41% in TNF experienced and 52% and 62.5% in TNF naive patients. Clinical trials may not however reflect real world experience.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted according to PRISMA guidelines to assess the real-world effectiveness and safety of UST in luminal CD based on current licensing approvals. A systematic literature search was performed using MEDLINE, EMBASE and conference proceedings from inception to 17 March 2021. Random-effects meta-analysis was used to assess clinical response, clinical remission, corticosteroid-free clinical remission (CFCR), biochemical remission and mucosal healing (MH) at weeks 8, 14, 26 and 52. Safety profile as well as rates of primary non-response (NR), secondary loss of response (LOR) and dose-intensification were also evaluated.
Results
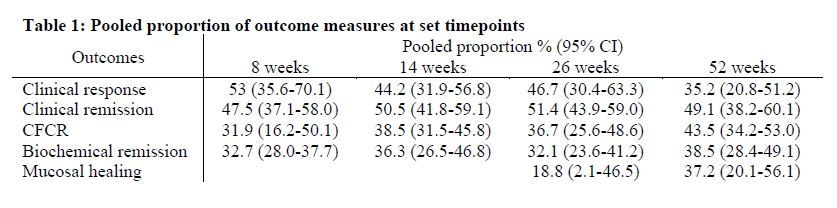
4,957 studies were screened with 36 studies (22 full text articles and 14 abstracts) meeting inclusion criteria, comprising 3,821 patients in total. Pooled outcome measures for clinical response, clinical remission, CFCR and biochemical remission at weeks 8, 14, 26 and 52 as well as MH at weeks 26 and 52 are reported in Table 1. UST was discontinued in 12.0% (95%CI, 7.3%-17.8%) during the follow-up period with over half attributable to failure of response. The overall safety profile was favourable compared to clinical trials, with a pooled adverse events rate of 14.6% (95%CI, 9.8%-20.2%). Primary NR and LOR were observed in 10.7% (95%CI, 6.6%-15.6%) and 12.7% (95%CI, 3.5%-26.5%), respectively. UST dose was intensified in 25.6% (95%CI, 11.3%-43.4%) of patients during follow-up.
Conclusion
This systematic review and meta-analysis of real-world studies demonstrates clinical effectiveness and safety of UST for CD comparable to that observed in clinical trials, supporting the use of UST in CD.
Reference:
1. Feagan BG et al. N Engl J Med 2016; 375:1946-1960 DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1602773