P596 Risk of colorectal cancer and other malignancies in association with the use of thiopurines, tumour necrosis factor antagonists or mesalazine
S. Timeus1, R. Laoun2
1Tillotts Pharma AG, Drug Safety, Rheinfelden, Switzerland, 2Tillotts Pharma AG, Medical Affairs, Rheinfelden, Switzerland
Background
Mesalazine, thiopurines and TNF antagonists play an important role in management of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). It is generally accepted that longstanding ulcerative colitis (UC) is associated with an increased risk of colorectal cancer (CRC). In addition to colorectal cancer, there are data that suggest that IBD is also associated with an increased risk of extra-intestinal malignancies but the results are inconclusive. The evidence concerning the effects of mesalazine on the risk of CRC in IBD patients remains conflicting.
Methods
In this review, cancer-reported outcomes with IBD drugs reported to FAERS (USA) were extracted for adalimumab, infliximab, thiopurines and mesalazine and compared with all other 25’382 drugs in the database. The data were used to calculate reporting odds ratio (ROR) and 95% CI for CRC, lymphoma, Hodgkin’s disease and all cancers outcomes. A sub-analysis was conducted to include patients exposed to mesalazine alone without IBD co-medications.
Results
The databases contained approximately 17 million reports for all drugs of which 401’084 were for adalimumab, 121 562 for infliximab, 11’985 for mesalazine, and 25’286 for thiopurines. Of these, a total of 259 757 concerned cancer-related AEs associated with the drugs under consideration. All IBD drugs were associated with a positive ROR for CRC with infliximab presenting the highest point estimate 8.01 (CI 95% 7.48–8.59) and adalimumab the lowest 2.52 (CI 95% 2.35–2.69). Considering patients exposed to only mesalazine, this association remained positive at 2.39 (CI 95% 1.58–3.59). For lymphoma, all IBD drugs also showed a positive ROR where thiopurines were associated with the highest 7.25 (CI 95% 6.69–7.84) and mesalazine with the lowest 1.46 (CI 95% 1.14 -2.73) point estimate. With regards to patients only exposed to mesalazine, the association showed protective effect, 0.24 (CI 95% 0.13–0.47). For Hodgkin’s disease again all IBD drugs showed a positive ROR where thiopurines were associated with the highest 34.65 (CI 95% 28.88–41.59) and adalimumab with the lowest 4.98 (CI 95% 4.39 -5.65) point estimate. In patients only exposed to mesalazine, no association 0.66 (CI 95% 0.09–4.66) was observed. Considering all cancers only positive ROR were observed where infliximab was associated with the highest 7.31 (CI 95% 7.17–7.45) and mesalazine with the lowest 1.33 (CI 95% 1.17–1.51) point estimate. In patients only exposed to mesalazine, a protective effect 0.73 (CI 95% 0.61–0.88) was observed.
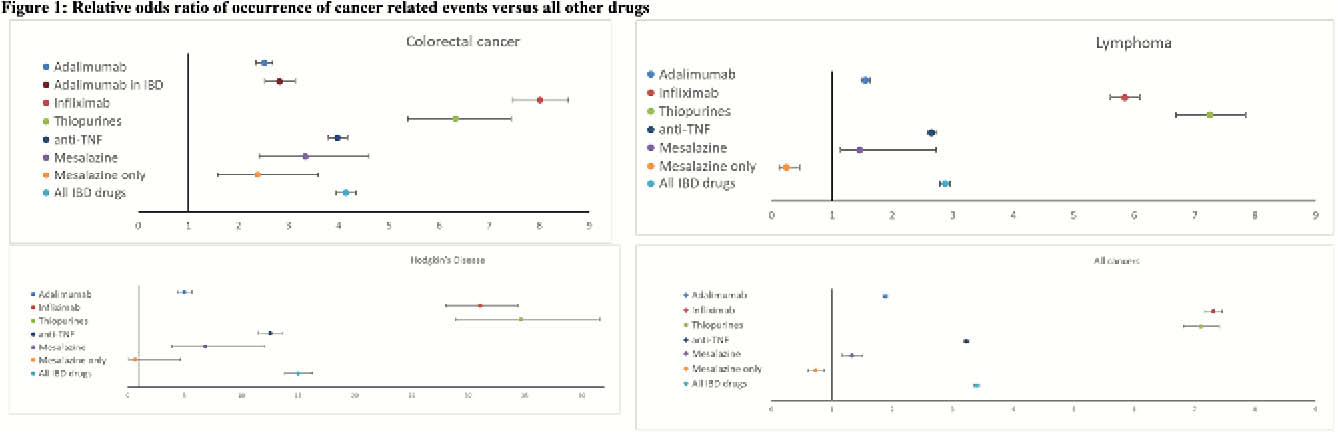
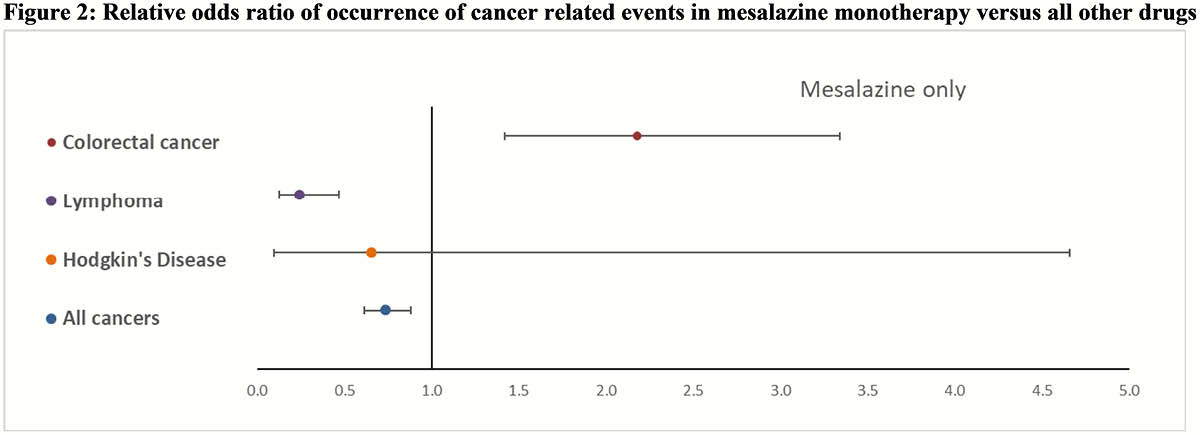
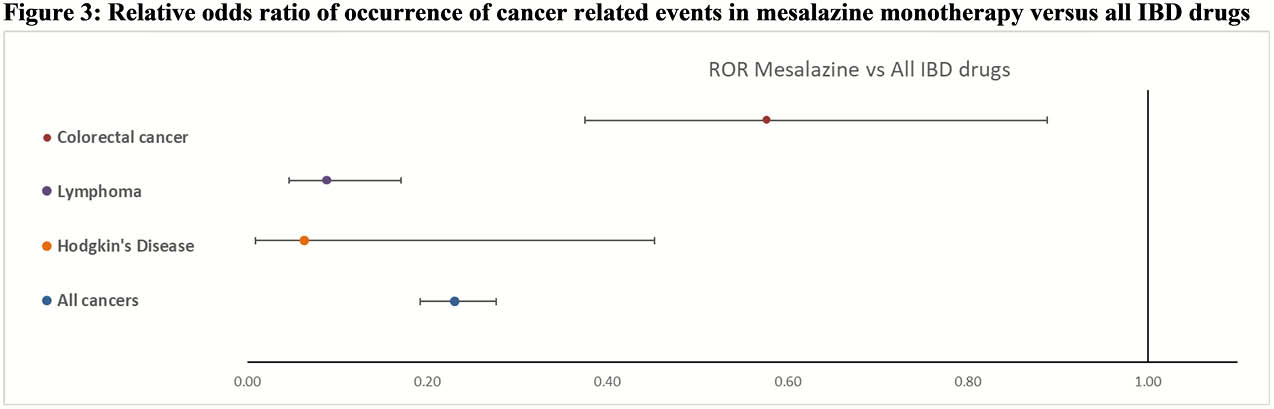
Conclusion
FAERS data showed an association between reported occurrence of cancer and the drugs under consideration. Considering patients only exposed to mesalazine the odds ratio was positive only for colorectal cancer but lower than all other IBD drugs.


