P686 Outcomes of COVID-19 among patients with inflammatory bowel diseases and the influence of IBD-related medications– A Danish prospective population-based cohort study
Attauabi, M.(1,2,3);Dahlerup, J.F.(4);Poulsen, A.(5);Rosager Hansen, M.(6);Vester-Andersen, M.K.(7);Eraslan, S.(3);Prahm, A.P.(5);Pedersen, N.(8);Larsen, L.(9);Jess, T.(9,10);Neumann, A.(11);Haderslev, K.V.(12);Molazahi, A.(13);Lødrup, A.B.(14);Glerup, H.(15);Oppfeldt, A.M.(16);Jensen, M.D.(17);Theede, K.(1,2);Kiszka-Kanowitz, M.(1,2);Seidelin, J.B.(3);Burisch, J.(1,2);
(1)Copenhagen University Hospital- Hvidovre, Gastrounit- Medical Section, Hvidovre, Denmark;(2)University of Copenhagen- Hvidovre Hospital, Copenhagen Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Children- Adolescents and Adults, Hvidovre, Denmark;(3)Herlev Hospital- University of Copenhagen, Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Herlev, Denmark;(4)Aarhus University Hospital, Department of Hepatology and Gastroenterology, Aarhus, Denmark;(5)Bispebjerg University Hospital, Digestive Disease Center, Copenhagen, Denmark;(6)North Zealand University Hospital, Department of Gastroenterology, Frederikssund, Denmark;(7)Zealand University Hospital, Department of Internal Medicine, Koege, Denmark;(8)Slagelse Sygehus, Department of Gastroenterology, Slagelse, Denmark;(9)Aalborg University Hospital, Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Aalborg, Denmark;(10)Aalborg University Hospital, National Center of Excellence for Molecular Prediction of Inflammatory Bowel Disease PREDICT- Department of Clinical Medicine, Aalborg, Denmark;(11)Region Hospital Viborg, Department of Internal Medicine, Viborg, Denmark;(12)Rigshospitalet- Copenhagen University Hospital, Department of Gastroenterology, Copenhagen, Denmark;(13)Holbaek Hospital, Department of Internal Medicine, Holbaek, Denmark;(14)Region Hospital West Jutland- Herning, Department of Internal Medicine, Herning, Denmark;(15)Region Hospital Silkeborg, Department of Internal Medicine, Silkeborg, Denmark;(16)Region Hospital Horsens, Department of Internal Medicine, Horsens, Denmark;(17)Lillebaelt Hospital- Vejle, Department of Internal Medicine- Section of Gastroenterology, Vejle, Denmark; Danish COVID-IBD Study Group
Background
Population-based data regarding outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) among patients with ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease (CD) remain limited.
Methods
We conducted a population-based study investigating the outcomes of COVID-19 among patients with UC and CD in Denmark. The Danish COVID-19 IBD Database is an extensive population-based database which prospectively monitors the disease course of laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 among patients with UC and CD. Severe COVID-19 was defined as COVID-19 necessitating intensive care unit admission, ventilator use, or death, while adverse COVID-19 was defined as requirement of COVID-19 related hospitalization. Regression analysis was adjusted for age, sex, disease type, disease activity, cardiovascular disease, and corticosteroids. Outcomes of COVID-19 among patients with UC and CD were compared with those among the background population covering all incidents of COVID-19 in Denmark.
Results
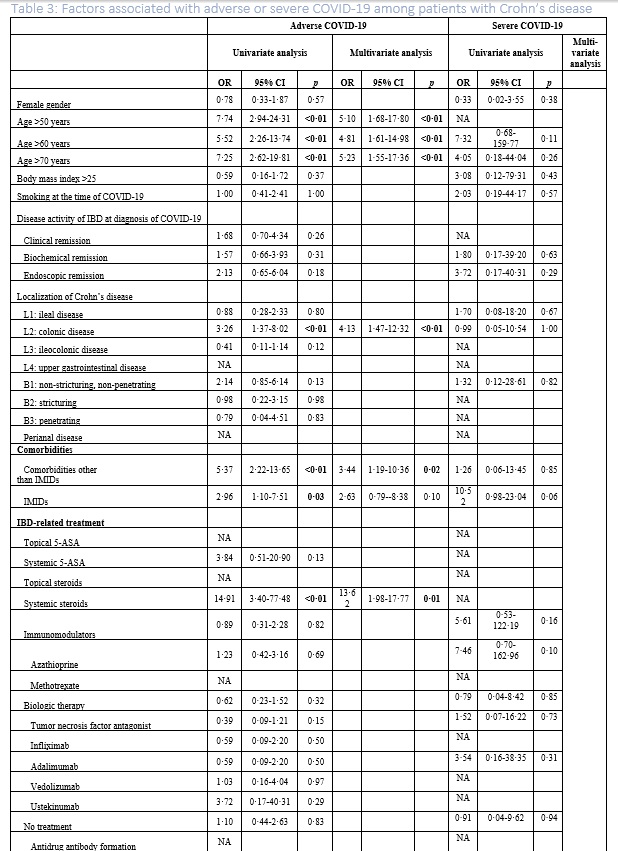
The study included 319 patients with UC and 197 patients with CD from January 28th, 2020, to April 1st, 2021. Baseline characteristics are presented in Table 1. A significantly higher risk of COVID-19-related hospitalization was observed among patients with UC (N=46(14.4%), RR=2.49 (95%CI 1.91-3.26)) and CD (N=24(12.2%), RR=2.11 (95%CI 1.45-3.07)) as compared with the background population (N=13,306 (5.8%)). A similar pattern was observed for admission to intensive care (UC: N=8(2.51%), RR=27.88 (95%CI 13.88-56.00); CD: N=3 (1.52%), RR=16.92 (95%CI 5.46-52.46)) (Figure 1). The association between these outcomes and IBD-related clinical characteristics and treatments is presented in Tables 2-3. As shown, none of the IBD-related medications were associated with severe COVID-19 in univariate and multivariable analysis. However, systemic steroids were found to be associated with an increased risk of adverse COVID-19 among patients with CD (adjusted odds ratio (aOR)=13.62 (95% CI 1.98-17.77)). 


Conclusion
This Danish population-based study on COVID-19 outcomes among patients with UC and CD demonstrated severe COVID-19 among only a minority of patients, which was not associated with IBD-related medications. Apart from systemic steroids, this study encourages continued use of IBD therapy to prevent IBD relapse and complications.
- Posted in: Poster presentations: Epidemiology 2022


