P699 The concordance of Short Form-36 Health Survey scores with Mayo scores in the tofacitinib ulcerative colitis clinical programme
M.C. Dubinsky1, A.G. Bushmakin2, J.C. Cappelleri2, J. Woolcott3, P. Sharma4, E. Maller3, L. Salese3, A. Armuzzi5
1Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York, USA, 2Pfizer Inc., Groton, Connecticut, USA, 3Pfizer Inc., Collegeville, Pennsylvania, USA, 4Pfizer Inc., New York, New York, USA, 5IBD Unit- Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli IRCCS, Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Rome, Italy
Background
The Short Form-36 Health Survey version 2 (SF-36v2) is a generic health-related quality-of-life (HRQoL) instrument [1]. Tofacitinib is an oral, small molecule JAK inhibitor for the treatment of ulcerative colitis (UC). In these exploratory analyses the concordance between total and partial Mayo scores and SF-36v2 scores was evaluated in patients with UC in the Phase 3 tofacitinib 8-week OCTAVE Induction 1&2 (NCT01465763; NCT01458951) and 52-week OCTAVE Sustain (NCT01458574) studies.
Methods
A repeated measures regression model was used to evaluate the relationship between total and partial Mayo scores (as predictor) and SF-36v2 component and domain scores. A sensitivity analysis to assess the linearity assumption was performed using Mayo score as a categorical anchor (represented by integer values 0–12 [total] or 0–9 [partial]). Previous analyses identified clinically important differences (CIDs) in total and partial Mayo scores as changes of 3 points and 2.25 points, respectively [2]. Mean differences in SF-36v2 component and domain scores were compared with their recommended group-level CID thresholds [3].
Results
Clinically meaningful differences of 3 points and 2.25 points in total and partial Mayo scores, respectively, were generally associated with clinically meaningful differences in SF-36v2 component and domain scores, with the exception of Role-Emotional with partial Mayo score in the pooled induction studies and with total Mayo score in the maintenance study. In the induction studies, a 3-point difference in total Mayo score was associated with a mean difference exceeding CIDs in both the SF-36v2 Physical Component Summary score (mean improvement 4.5; 95% confidence interval [CI] 4.2, 4.7) and Mental Component Summary score (mean improvement 5.0; 95% CI 4.6, 5.3). Results were closely aligned when Mayo score was used as a categorical or continuous anchor, supporting a linear relationship between Mayo score and SF-36v2 scores (Figure). Similar results were observed in the maintenance study, and when assessing the relationship of partial Mayo score with SF-36v2 scores.
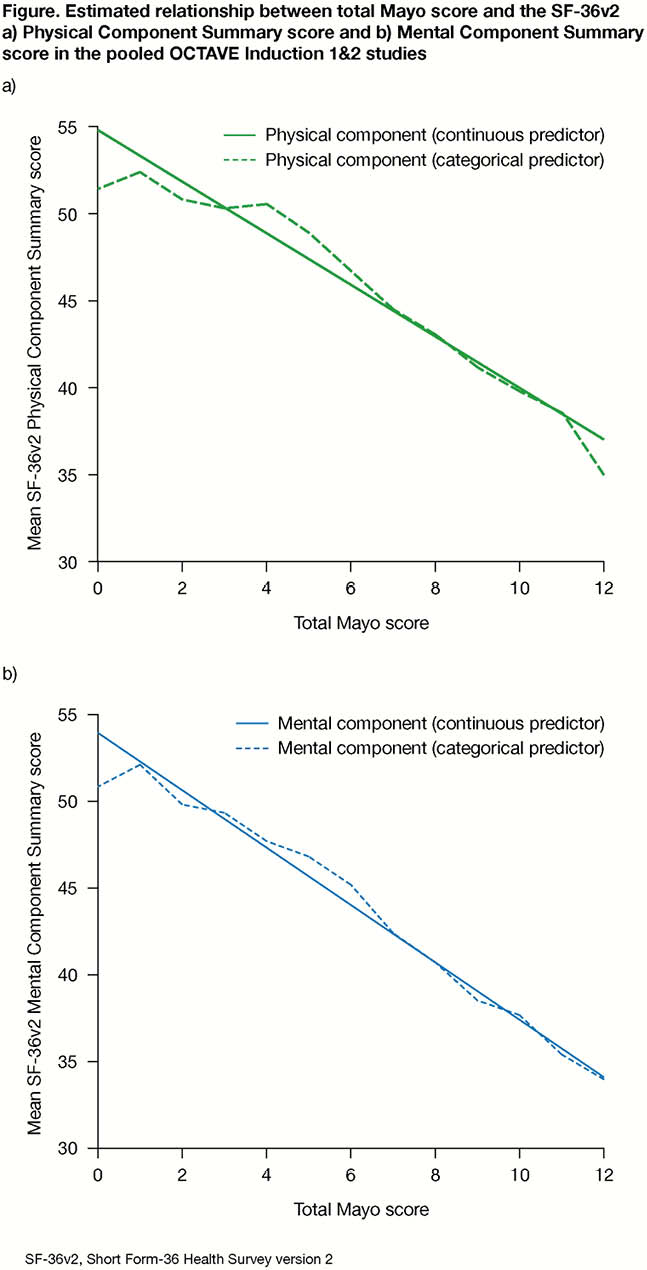
Conclusion
Clinically meaningful decreases in disease activity, as measured by Mayo score, were associated with clinically meaningful benefits in HRQoL, as measured by SF-36v2 component and domain scores. These findings highlight the impact that disease activity has on HRQoL and may assist with articulating the treatment effect of tofacitinib on specific domains.
Ware JE
Lewis JD
Ware JE


