P747 The impact of COVID-19 on patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A population-based study using artificial intelligence.
Moralejo Lozano, Ó.(1)*;Beneyto Martín, P.(2);Abanades Tercero, M.(1);Muñoz Rosas, C.(1);Ruano Díaz, L.(1);Salmoral Luque, R.(1);Gómez Rodríguez, R.(1);
(1)Hospital Universitario de Toledo, Gastroenterology and Hepatology Aparato Digestivo, Toledo, Spain;(2)Hospital Universitario de Toledo, Research Department, Toledo, Spain;
Background
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has been a pandemic that is still very prevalent. Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) represent a special population considering their already altered immune system and their exposure to several immunosuppressive therapies. We pretend to study the impact of COVID-19 on IBD patients in our community, Castilla-La Mancha (a region in central Spain).
Methods
Retrospective observational study using an artificial intelligence with natural language processing capability, the SAVANA manager, we analyzed data from 1 808 010 patients with Electronic Medical Records (EMR) within the public health system of Castilla-La Mancha from March 1st 2020 to January 1st 2021. Data on demographic characteristics, hospitalization, ICU admission and mortality were collected. We compared COVID outcomes between IBD and non-IBD patients. We compared COVID outcomes in IBD patients according to their treatment (comparing each treatment group to those IBD patients with no treatment); we considered: immunomodulators (azathioprine, mercaptopurine, methotrexate), antiTNF alone or combined with immunomodulator, vedolizumab, ustekinumab and tofacitinib; mesalazine and corticosteroids were not analyzed.
Results
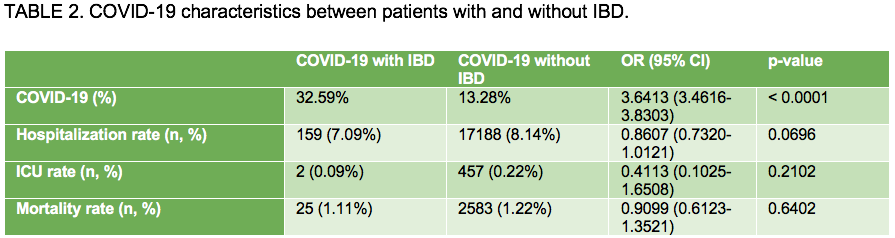
2 243 patients with IBD suffered COVID-19, compared to COVID-19 cases without IBD there were less females, they suffered more arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, obesity, or tabacco use (TABLE 1). And yet, despite these being proven risk factors for worse outcomes for COVID-19, no differences were appreciated in hospitalization rate, ICU admission, or mortality between those with or without IBD (TABLE 2). COVID-19 was more frequent in IBD patients (32.59 vs 13.28%). Comparing IBD patients with COVID-19 according to their treatments (TABLE 3), vedolizumab is the only treatment with a higher risk for COVID-19 infection, however the hospitalization risk for vedolizumab is lower than for those without it. Immunomodulators do also have a lower hospitalization risk both alone or in combination with antiTNF, no differences were found for antiTNF monotherapy, ustekinumab or tofacitinib. ICU rate and mortality are no different between treatments, except for tofacitinib (0.00% ICU rate, 10.00% mortality), however the small number of patients using this treatment may bias this result.

Conclusion
COVID-19 in IBD patients is no different in hospitalization, ICU admission or mortality compared to non-IBD population. IBD patients exposed to immunomodulators and vedolizumab have less hospitalization risk than those not exposed, no differences were found for antiTNF alone or ustekinumab. The impact of tofacitinib in COVID outcomes requires further investigation.


