P833 Bacterial mucosa-associated microbiome in inflamed and proximal non-inflamed ileum of patients with Crohn’s disease
M. Olaisen1,2, A. Flatberg1, A. van Beelen Granlund1,3, E.S. Røyset1,4, T.C. Martinsen1,2, A.K. Sandvik1,2,3, R. Fossmark1,2
1Department of Clinical and Molecular Medicine- Faculty of Medicine and Health Science, NTNU - Norwegian University of Sciences and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 2Department of Gastroenterology, St. Olav’s Hospital- Trondheim University Hospital, Trondheim, Norway, 3Centre of Molecular Inflammation Research, NTNU - Norwegian University of Sciences and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 4Department of Pathology, St. Olav’s Hospital- Trondheim University Hospital, Trondheim, Norway
Background
The microbiota most likely has an essential role in the pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease (CD). While faecal diversion after ileocecal resection (ICR) protects against CD recurrence, re-exposure triggers inflammation. After ICR, the majority of patients develop recurrence in the neoterminal ileum and the ileal microbiome is of particular interest. We have therefore assessed the mucosa-associated bacterial microbiome in the inflamed and non-inflamed ileum of patients with CD.
Methods
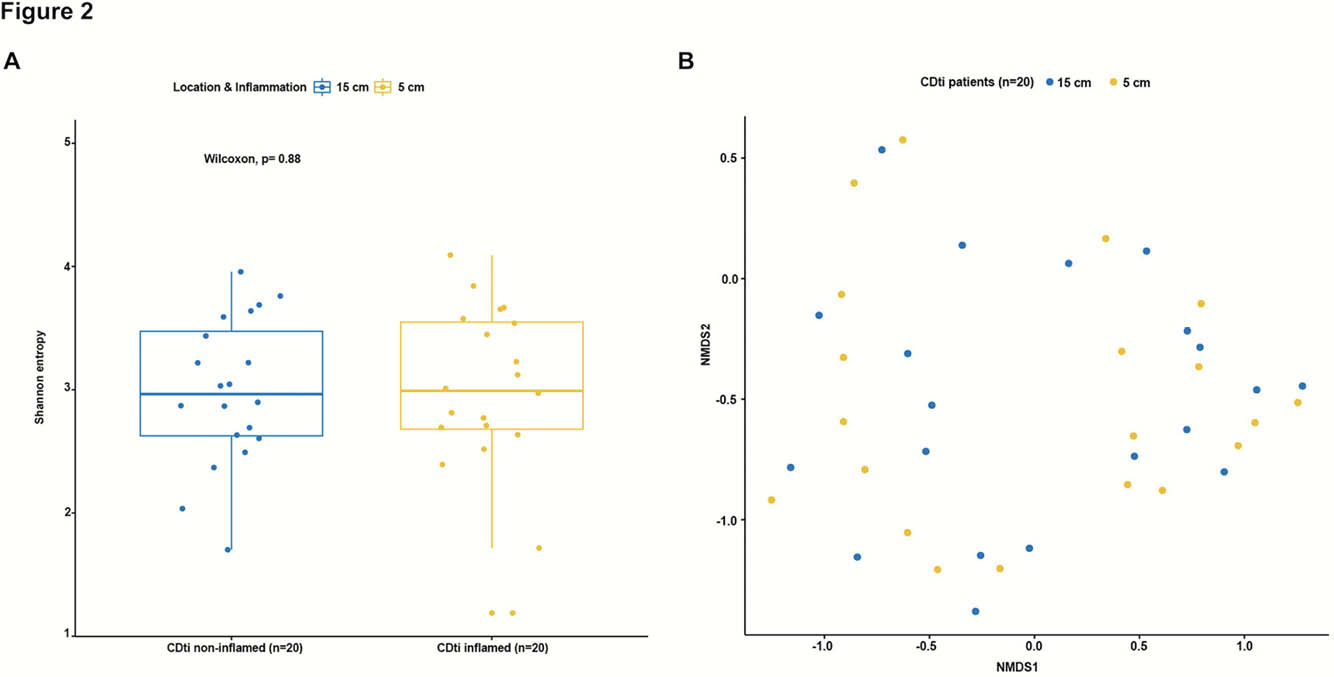
Patients with an established diagnosis of CD undergoing ileocolonoscopy and healthy controls (HC) referred for colonoscopy due to rectal bleeding or screening for disease, but without any detected gastrointestinal pathology were invited to participate. Exclusion criteria included use of antibiotic treatment for the past 2 months. Mucosal pinch biopsies were sampled 5 cm and 15 cm orally of the ileocecal valve or ileocolic anastomosis for comparisons within the same patients. The biopsies were analysed by 16S rRNA sequencing, α- and β-diversity was assessed by Shannon entropy and Bray-Curtis dissimilarity index respectively. Histologic inflammation was graded.
Results
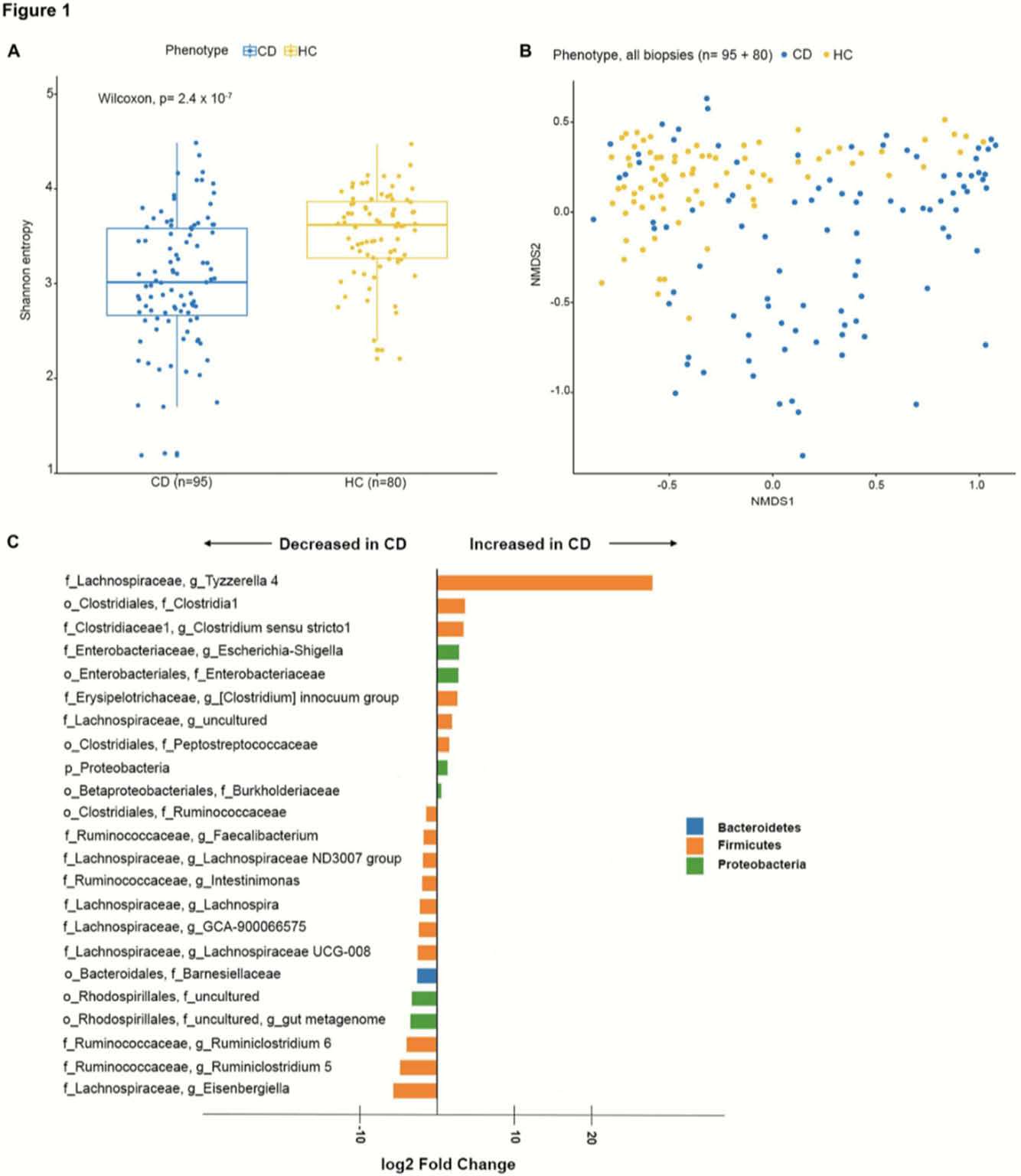
Fifty-one CD patients, where of 32 with previous ICR, and 40 HC were included in the study. Of the 51 CD patients, 20 had terminal ileitis, with endoscopically inflamed mucosa at 5 cm and normal appearing mucosa at 15 cm and no history of upper GI disease involvement. Seven CD patients had ileal stenosis. CD patients (
Conclusion
23 taxa were differentially expressed in CD compared with HC. The ileal mucosa-associated microbiome is similar assessed by both α- and β-diversity in the inflamed mucosa and the proximal non-inflamed mucosa within the same patients. Our results support the concept of CD specific microbiota alterations and demonstrate that neither ileal sub-location nor endoscopic inflammation itself influence the mucosa-associated microbiome.


